What is Personality disorder and it’s Cluster A,B and C
Wednesday January 5, 2022 |
Personality Disorder: Inability to follow social conventions or more?
Personality is something that makes each one of us different. Our reactions to things, style of behavior, thoughts, feelings, worldview, and how we interact in relationships reflect our personality. A healthy personality enables an individual to function better in everyday life. Every one of us experiences stress at a point in time, but a healthy personality helps us overcome it or face the challenges strongly and move on.
It becomes challenging for someone with a personality disorder to keep up with the ordinary life, and their attitude towards life changes. This article will give you an overview of the illness, types, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and available treatment.
An overview of the illness
A disorder is characterized by chronic coping mechanisms in an inappropriate, stereotyped, and maladaptive manner. It include endured and persistent patterns of behavior and thoughts, not unusual episodes.
Personality disorders are a group of mental health issues characterized by inflexible atypical styles of thinking, feeling, and behaving. These inner experiences and how you react often differ from the expectations of the society you are a part of.
Is a personality disorder a mental illness? Personality disorders are mental health illnesses that involve long-duration patterns, thoughts, and behaviors that are usually unhealthy and inflexible. It can further cause other mental illnesses such as anxiety, stress, or depression.
People with personality disorders may have difficulty communicating with others and dealing with everyday life problems in a way considered normal by their cultural group. There are chances that you are not fully aware of the discrepancies between their thoughts & behaviors and those accepted by society.
If you have any personality disorder, you may find it challenging to have a worldview similar to others. As a result, you may find it challenging to participate in social, educational, and family activities. These behaviors and attitudes may cause issues and limitations in social encounters, relationships and make it difficult for you to operate in school or work settings. It may also make you feel isolated, increasing the risk of depression and anxiety.
Can personality disorder be cured? Yes! They are treatable conditions. Often a balanced combination of talk therapy and personality disorder medications can go a long way in aiding you with one of these medical conditions.
Personality Disorder Symptoms
Personality disorder types are grouped into clusters, depending on similar characteristics and symptoms. People with this health condition also have signs and symptoms of at least one more personality disorder. It is not necessary that all the symptoms listed for a specific disease be diagnosed.
What personality disorder do I have? If you also ask this question yourself, you may make a rough guess by checking what personality disorder cluster you belong to. Every group has different criteria if you have this medical condition.
Cluster A, B, and C personality disorders
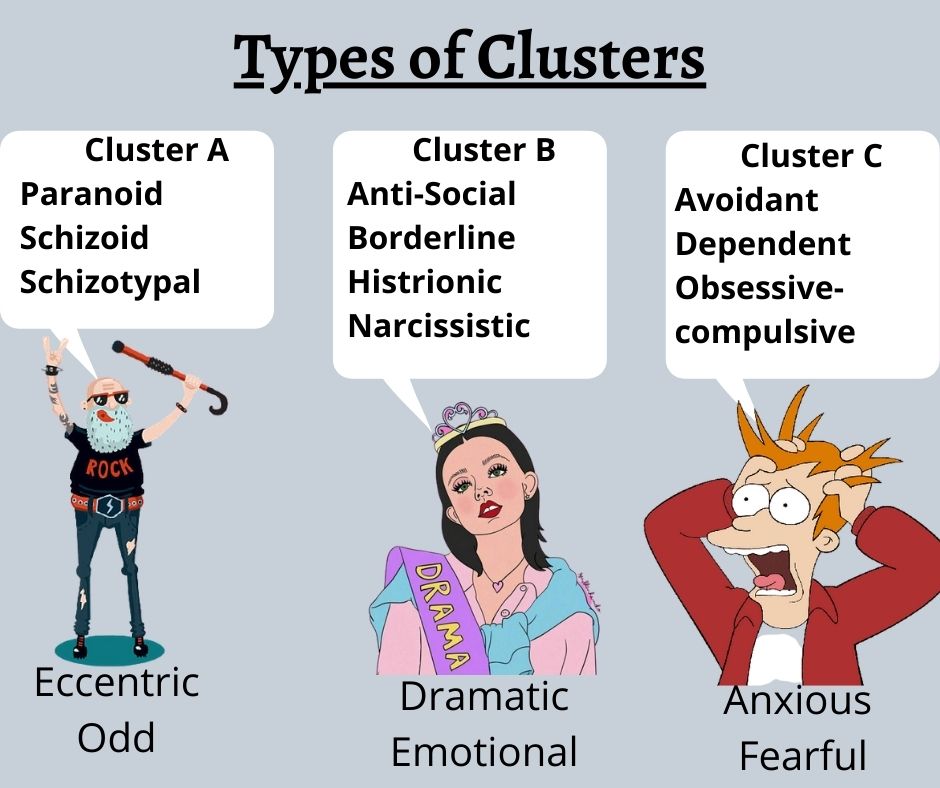
Personality Disorders Cluster A:
According to Mental Health America (MHA), it comprises behavior that seems odd, eccentric or suspicious to others, according to Mental Health America (MHA). It includes the following disorders:
Paranoid personality disorder: People with this medical condition may be suspicious of their motives and distrust others.
Schizoid personality disorder: In this one, the individual can display minimum interest in forming personal relationships or interacting socially. They can experience difficulty interpreting social cues, and they appear as emotionally distant people.
Schizotypal personality disorder: In this mental health condition, people often believe that they can change by influencing other people or events with their thoughts. They misinterpret others and take their behavior as insulting, and it causes them to give inappropriate emotional responses. These people also avoid having an intimate relationship.
Personality Disorder Cluster B
It comprises behavior that is emotional, dramatic, impulsive, or erratic. It includes the following disorders:
Antisocial personality disorder: In this condition, individuals manipulate others or treat them without expressing remorse for their actions. They can engage in cunning or dishonest behavior such as stealing and lying, and they are more close to the risk of alcoholism or heavy drug use.
Borderline personality disorder: An individual diagnosed with this condition often feels empty and abandoned, even after having family or community support. They may experience difficulty dealing with stressful situations and might have episodes of paranoia. They can also engage in impulsive and risk-taking behavior, including binge drinking and gambling.
Borderline personality disorder: It usually develops if you are a victim of physical, emotional, or sexual abuse or if you were exposed to long-term distress or fear in childhood. Other factors include being neglected by one or both parents and growing up with a family member having a severe mental health condition, such as bipolar disorder, alcoholism, or any substance use disorder.
Histrionic personality disorder: People with this health condition frequently get more attention by being overdramatic or provocative. These people easily get influenced by others and are sensitive to criticism or disapproval.
Narcissistic personality disorder: People with this personality disorder often believe that they are much important than any other person. They keep exaggerating their achievements unnecessarily and may brag about their success or attractiveness. Other primary symptoms may include a deep need for admiration lacking empathy for other people.
Personality Disorders Cluster C
People with these disorders have the underlying behavior of anxiety and fear as they are usually anxious. It includes:
Avoidant personality disorder: Individuals with this personality disorder usually have feelings of inferiority, inadequacy, or unattractiveness. They may feel they are not good enough and dwell on criticism from others. They also avoid participating in new activities and do not make new friends.
Dependent personality disorder: In this medical condition, an individual depends on other people to meet almost all their physical and emotional needs. They avoid staying alone usually and need regular reassurance while making decisions. These people are more likely to tolerate any physical or verbal abuse.
Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder: People dealing with this mental health condition have an overwhelming urge to put everything in order. They usually freak out when things are not in order. They firmly stick to rules and regulations and feel highly uncomfortable when perfection is not achieved. They can even neglect a personal relationship and put all their efforts into making a project perfect.
What personality disorder is a control freak? People with Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder are considered to control aberrations due to their nature of keeping things in order and overreacting when things are not happening precisely as they want.
Personality Disorder Causes
Your personality is a combination of thoughts, emotions, and how you behave. Your personality is the way you understand and relate to the outside world and how you perceive yourself. The reason behind these disorders is still unknown, but it is believed that they may be triggered due to genetic and environmental factors, most prominently childhood trauma.
Personality shapes in childhood through a combination of your genes and environment. Personality disorder genetic: Specific personality traits may be passed to you by your parents through inherited genes. Sometimes, these traits are called temperament. Your environment involves everything you grew up in, events, and relationships with relatives and friends.
What are the Risk Factors with personality disorders?
Although the actual cause of these disorders is still not known, specific factors are likely to contribute to the development of triggering of personality disorders, including:
- Diagnosis with childhood conduct disorder
- Family history of personality disorders or other mental health conditions
- Unstable, abusive, or chaotic life during the childhood
- Variations in brain chemistry and composition
Complications
Personality disorders can significantly disrupt the diagnosed person’s regular life and people who care about that affected person. These disorders may cause problems with personal and professional relationships at home and work, can result in social isolation, alcoholism, or any substance use disorder.
Untreated personality disorders can lead to significant personal and social loss, including hospitalizations, lack of productivity, significant unhappiness, and imprisonment in your castle. If not getting proper treatment on time, such individuals can show violent or self-destructive behavior, even commit suicide.
Measures to diagnose personality disorders
Doctors or mental healthcare professionals reference the Diagnostic and Statistics Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) to diagnose mental health conditions. Each personality disorder has different criteria to get clinically diagnosed, while you may also try a personality disorder test online with some useful apps.
A mental healthcare provider or primary care health expert may ask you questions depending upon these criteria to check the type of personality disorder. To make a precise diagnosis, the behaviors and feelings of an individual must be consistent across several life circumstances. They should have significant distress and impairment in at least two of the below-mentioned areas:
- the way you perceive yourself and other people
- how appropriate your emotional responses are
- how you react in public and deal with other people
- how efficient you are while controlling your impulses
In some cases, your medical healthcare provider may ask you for blood tests to determine whether a medical condition is causing your symptoms. In some other cases, the primary healthcare expert or mental health professional may order a screening test for drugs or alcohol if they think some substances are the reason behind your symptoms.
What are the possible treatments for personality disorders?
The four most recommended ways can help treat these mental health conditions. It includes psychotherapy, medication, home remedies, lifestyle changes, and hospitalized or institutionalized sessions. Here, we will have a look at all the available treatment options:
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, can help in personality disorders management. During a psychotherapy session, you and the therapist can talk about your condition, as well as your thoughts and feelings. This method can provide insight into how to manage your mental health condition and behaviors that disturb your daily life.
There are several types of psychotherapy, among which dialectical behavior therapy includes group and individual sessions where individuals learn skills to manage the symptoms. At the same time, cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) is a talk therapy method that makes you more aware of your behavior and thought patterns, helping you control them better. Two other psychotherapy methods are:
- Psychoanalytic therapy: These talk therapy sessions focuses on uncovering unconscious or buried memories and emotions and helping you resolve them.
- Psychoeducation: This method focuses on helping you better understand your health condition and what it involves.
Medication
There are not any general or FDA-approved medications for personality disorder treatment. However, specific categories of prescription medicines might help in reducing several personality disorder symptoms, such as:
- Antidepressants: They may help if you have a depressed mood, impulsivity, anger, irritability, or hopelessness associated with personality problems.
- Mood stabilizers: They stabilize mood and help even out mood swings or reduce impulsivity, irritability, and aggression.
- Antipsychotic (neuroleptic) medications: These may aid if your symptoms include psychosis (losing touch with reality) or if you have anxiety or anger problems.
- Anti-anxiety drugs: They may help if you have agitation, anxiety, or insomnia. But it would help if you were careful as they can increase impulsive behavior in some cases. It is best to avoid them in specific personality illness types.
Hospitalized and Institutionalized Sessions
In some cases, a severe personality disorder may need you to be admitted to a hospital or mental care institute for psychiatric treatment. Hospitalization or institutional sessions are generally suggested when individuals are unable to take care of themselves or are in danger of causing harm. After stability in your condition in the hospital, your medical healthcare provider may recommend a daycare program, outpatient treatment, or residential program.
Lifestyle changes and home remedies
Along with an effective professional treatment plan, consider following the below strategies to tackle personality issues:
- Actively participating and cooperating with your health professional shows your efforts to manage this condition. Avoid skipping any therapy session; convince yourself even if you do not feel like going. Make treatment goals and try achieving them.
- Read personality disorder books: To understand these disorders better, read books written on this topic.
- Watch personality disorder movies: Several movies are produced on sensitive topics these days. You may pick a good film on this topic that will help you understand this mental health condition.
- Stay active: Physical activity can help cope and relieve several symptoms, such as stress, anxiety, and depression. It can also counteract the adverse effects of some psychiatric drugs that may cause weight gain. Consider swimming, walking, jogging, gardening, or participating in any physical activity you enjoy including dance.
